Autonomous AI Agents Explained for Business
A practical guide to autonomous AI agents. Learn how their architecture works, their real-world business impact, and how to integrate them into your operations.
Autonomous AI agents are sophisticated software programs that can independently reason, plan, and carry out complex tasks to hit specific goals, all without a human needing to guide every step. Think of them less as simple tools and more like highly capable digital employees.
So, What Are Autonomous AI Agents Really?

When many business leaders hear “AI,” their minds often jump to chatbots or basic automation scripts. Those are certainly useful, but they’re fundamentally reactive. They stick to a set of pre-written rules and only act when given a direct command.
An autonomous AI agent operates on a completely different level.
The key word here is autonomy. This isn’t just about following instructions; it’s about the agent having the built-in ability to perceive its digital environment, make decisions, and execute a whole sequence of actions to achieve a high-level goal.
Going Beyond Basic Automation
Let’s draw a parallel. Imagine the difference between a personal assistant and a seasoned project manager.
-
A personal assistant (like a chatbot or a script) waits for your command. If you tell it to send an email, it sends that one email. It’s brilliant at executing single, clearly defined tasks.
-
A project manager (the autonomous agent) is given a broad objective, like “launch the new marketing campaign.” From there, it takes over. It figures out the strategy, breaks the goal down into smaller tasks, coordinates resources, tracks progress, and even pivots when unexpected issues pop up.
This capacity to plan, adapt, and problem-solve is what truly separates autonomous agents from the pack. They don’t just mindlessly follow a script; they navigate complex situations and use their judgment to get to the finish line. This is a massive turning point for how we think about operational efficiency—moving from just executing tasks to orchestrating entire workflows.
Autonomous AI agents represent the next significant evolution in artificial intelligence, moving beyond conversational interfaces to systems that leverage AI to reason, plan, and complete tasks in tandem with – or on behalf of – humans.
Why This Matters For Your Business
This shift from instruction-based tools to goal-oriented agents unlocks a whole new level of strategic value. Instead of just automating isolated, repetitive actions, businesses can now automate entire complex processes from start to finish. For a more detailed breakdown, you can learn more about what an AI agent is by visiting what is an ai agent and see how they operate in a business context.
The potential applications are huge, promising major gains in both productivity and smarter decision-making. To get a better sense of how these agents can specifically help in the corporate world, it’s worth exploring more about AI agents for business https://nolana.com/articles/ai-agent-for-business. This isn’t just about doing the same things faster; it’s about building business operations that are more intelligent, resilient, and adaptive to change.
Deconstructing How Intelligent Agents Work
To really get what autonomous AI agents can do, we need to pop the bonnet and look at how they’re built. It’s not some mysterious “black box.” An intelligent agent is actually a structured system made of distinct modules, all working together. Think of it like different departments in a company, each with a specific job, collaborating to hit a major business goal.
At its core, an autonomous agent runs on a continuous loop, cycling through three essential phases: sensing its environment, deciding what to do next, and then actually doing it. This is the secret sauce that allows it to go from a big-picture objective to a series of concrete steps, all without a human needing to approve every single move.
The diagram below shows this core architecture, illustrating how the central AI brain connects to its “senses,” “thoughts,” and “hands.”
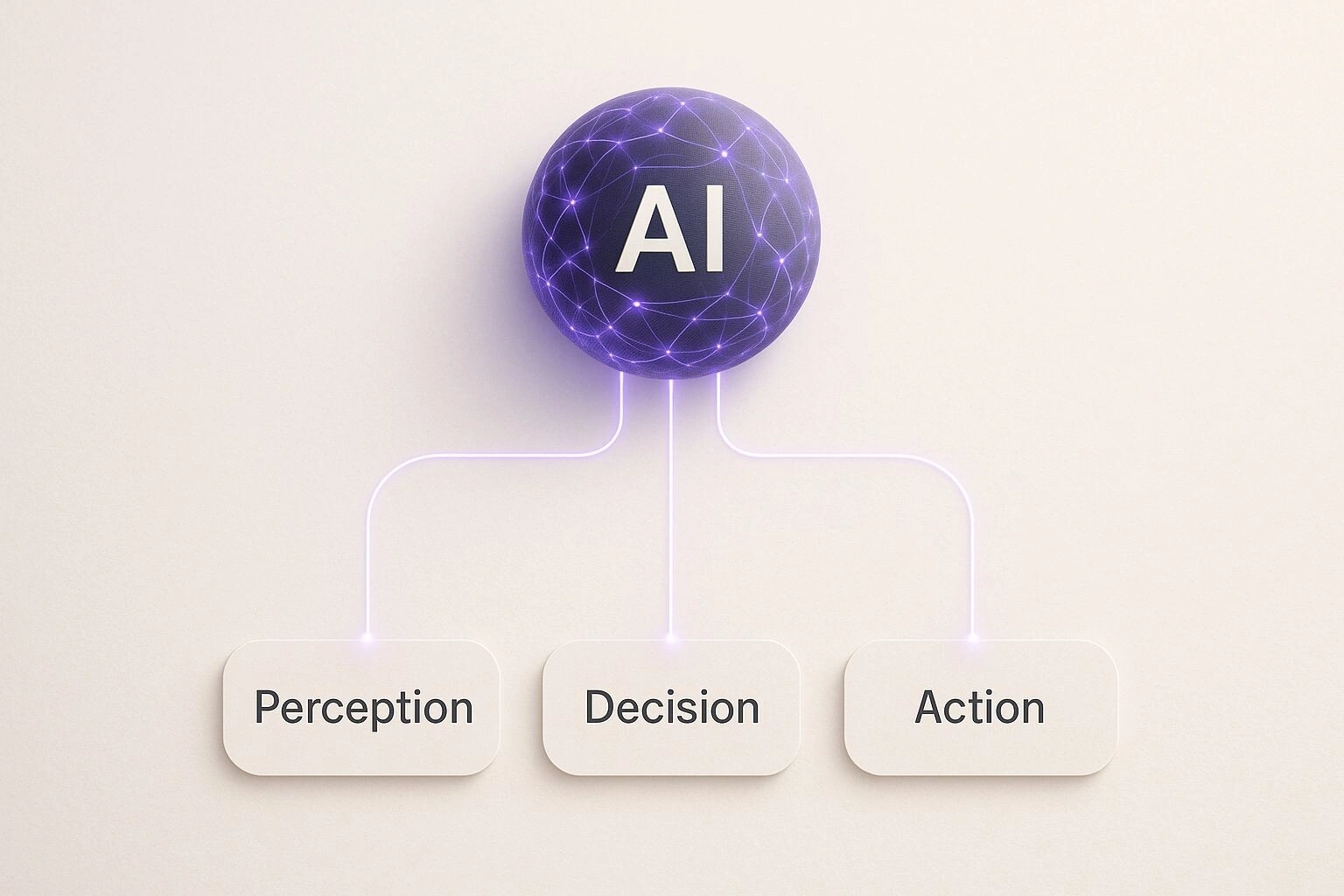
This really brings home the cyclical nature of the agent’s work. Data flows from perception to action, and the results of that action feed straight back into the agent’s perception, starting the loop all over again.
The Perception Module: Sensing the Digital World
First up is the perception module. Its job is to gather and make sense of data from its digital surroundings. This is the agent’s eyes and ears, constantly scanning for relevant information from sources like emails, databases, websites, system APIs, or direct user commands.
But this module doesn’t just hoover up raw data. It processes and organises it into a format the agent can actually use. For instance, it might pull key details from a PDF invoice, figure out the tone of a customer email, or spot a critical alert from a system monitoring tool. This first step is all about giving the agent situational awareness.
The Reasoning Engine: Planning and Decision-Making
Once the agent has a clear picture of its environment, the data flows to the reasoning engine—the agent’s brain. This is where the magic happens. Powered by Large Language Models (LLMs), this engine analyses the situation, breaks the main goal down into smaller, bite-sized tasks, and maps out a strategic plan.
To grasp the mechanics here, it helps to understand a few fundamentals, like how neural networks mimic the human brain. This engine is constantly weighing up the current state, the end goal, and the tools it has available to find the most efficient way forward.
A critical part of this is memory. Autonomous AI agents have both short-term and long-term memory, which is a game-changer.
- Short-term memory helps the agent keep track of the immediate context, like the flow of a single conversation or task.
- Long-term memory lets it store what it has learned from past jobs, allowing it to get better and smarter over time.
This ability to remember and learn from experience is what separates these agents from simple scripts. It can adapt its approach based on what worked—and what didn’t—in the past.
The real power of an autonomous agent isn’t just in doing tasks, but in its ability to self-correct. When an action doesn’t get the right result, the reasoning engine analyses the outcome, revises its plan, and tries something else.
The Action Module: Executing Tasks in the Real World
Finally, the action module takes the plan cooked up by the reasoning engine and puts it into motion. These are the agent’s hands, reaching out to interact with other digital systems to get things done. This module is the bridge between the agent’s decisions and real-world execution.
What an agent can do is defined by its toolkit. A sales agent might have tools to access a CRM, send emails, and book meetings. A finance agent, on the other hand, would have tools to talk to accounting software, pull reports, and process payments.
For example, if the goal is to “onboard a new client,” the action module might fire off a sequence of commands like these:
- Create a new client record in the CRM.
- Send a standardised welcome email via an email API.
- Schedule a kick-off meeting by connecting to the calendar software.
- Generate an initial invoice using the accounting platform.
This seamless cycle of perceiving, reasoning, and acting is precisely what allows autonomous AI agents to manage complex, multi-step processes with a degree of independence we just couldn’t achieve before.
Real-World Applications for Autonomous AI
It’s one thing to talk about the architecture of an autonomous AI agent, but where the rubber really meets the road is in solving tangible business problems. The abstract idea of an intelligent, goal-driven system clicks into place when you see how these agents are already delivering serious operational advantages.
Across departments, from finance to human resources, their ability to take on and manage complex, multi-step workflows is fundamentally changing how core business functions get done.
The strategic weight of this technology is impossible to ignore. A recent analysis points to autonomous AI agents as a top technological priority for Australian businesses in 2025. This isn’t just hype; it reflects their critical role in achieving operational scale and getting real-time business intelligence. As companies move past their initial experiments with generative AI, the conversation is shifting to embedding foundational tech like AI-ready data infrastructure and autonomous agents to build something sustainable and enterprise-wide.
Transforming Financial Operations
The finance department is a perfect starting point for agent-driven automation. It’s an area built on rule-based, data-heavy processes that have historically been manual, tedious, and prone to error. An autonomous agent can take these workflows and turn them into highly efficient, automated operations.
Think about financial reconciliation. For years, this meant teams of analysts painstakingly comparing transactions across different systems—bank statements, ledgers, payment gateways. It was a process that could drag on for days, with a constant risk of human error.
Now, you can give an autonomous financial agent a simple goal: “reconcile all accounts for last month.” From there, it gets to work.
- It accesses data from all the necessary financial systems using its built-in tools.
- It compares thousands of transaction records in a matter of minutes, not days.
- It instantly identifies any discrepancies and flags them for a human to review.
- Finally, it generates a complete reconciliation report without any manual intervention.
The result? The month-end close is dramatically faster, and financial analysts are freed up to focus on what really matters—strategic forecasting and spotting potential risks.
Optimising Human Resources and Recruitment
Human resources teams are constantly juggling a high volume of repetitive but crucial tasks, especially when it comes to hiring and onboarding. Autonomous AI agents can step in to manage the entire top-of-funnel recruitment process with very little human input, creating a faster and more consistent experience for candidates.
Give an agent a goal like, “fill the Senior Developer role,” and it can autonomously screen thousands of applications against the job description, reach out to qualified candidates by email to schedule interviews, and even run preliminary technical assessments.
This allows HR professionals to step away from the administrative grind and put their energy into strategic talent management. The agent handles the logistics, while the human team concentrates on meaningful conversations, final interviews, and making sure a candidate is the right cultural fit.
Enhancing Supply Chain Management
Modern supply chains are a web of complexity, constantly threatened by potential disruptions. An autonomous AI agent can serve as a digital watchtower, proactively managing and heading off these issues before they turn into expensive problems.
Picture a supply chain agent that monitors global shipping routes and supplier inventory in real-time. If it spots a potential delay—maybe from a weather event or a port shutdown—it doesn’t just send an alert. It autonomously figures out the impact on production schedules and starts looking for solutions.
The agent could:
- Pinpoint the affected shipments and calculate the downstream effects.
- Contact alternative suppliers from an approved list to check for availability.
- Analyse the cost and time differences of rerouting the shipment.
- Present a fully costed solution to a human manager for the final green light.
This kind of proactive problem-solving transforms the supply chain from a reactive function into a truly resilient and intelligent system.
To provide a clearer picture, here’s a breakdown of how these agents can be applied across different parts of a business.
Autonomous Agent Applications Across Business Functions
| Department | Use Case Example | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Finance | Automated Reconciliation: Agent compares transactions across ledgers, bank statements, and payment systems to identify and flag discrepancies. | Reduces manual effort, accelerates financial close times, and improves accuracy. |
| Human Resources | Recruitment Screening: Agent sifts through résumés, identifies top candidates based on set criteria, and schedules initial interviews. | Speeds up time-to-hire, reduces administrative burden, and ensures consistent screening. |
| Supply Chain | Proactive Disruption Management: Agent monitors logistics, identifies potential delays, and suggests alternative routes or suppliers. | Increases supply chain resilience, minimises downtime, and reduces costs from disruptions. |
| IT Operations | Automated Helpdesk: Agent triages IT support tickets, resolves common issues (like password resets), and escalates complex problems. | Improves employee satisfaction with faster response times and frees up IT staff for strategic projects. |
| Marketing | Campaign Orchestration: Agent manages multi-channel marketing campaigns, adjusting ad spend and messaging based on real-time performance data. | Optimises marketing ROI, improves campaign agility, and provides deeper performance insights. |
| Customer Service | Complex Query Resolution: Agent handles multi-step customer issues, accessing order history and knowledge bases to provide complete solutions. | Enhances customer experience, reduces wait times, and lowers operational costs. |
These examples are just the beginning. A major application that benefits almost every organisation is the ability to provide 24/7 customer support with AI agents, guaranteeing that help is always available. The core principle of autonomous problem-solving can be applied to nearly every business function, showing just how versatile these intelligent systems truly are.
Gauging the Real-World Impact on Your Business

It’s one thing to talk about what autonomous AI agents can do, but what really counts is translating that potential into tangible business outcomes. For any leader, the crucial question isn’t just “What’s the capability?” but “What’s the return on my investment?” To really see the benefits, you need to link agent deployment directly to bottom-line improvements and strategic growth using clear key performance indicators (KPIs).
The effects are often felt almost immediately, especially in departments bogged down by repetitive manual work. By taking over complex workflows, these agents cut right through operational bottlenecks, leading to noticeable cost reductions and faster project turnarounds. But the true value goes far beyond just getting things done quicker.
This level of automation frees up your most crucial resource: your people. It allows them to shift their focus to high-value work that demands creativity, strategic thought, and complex problem-solving. Imagine your team analysing market trends and innovating new processes instead of being stuck with data entry. That’s where the real growth happens.
Quantifying Gains in Operational Efficiency
To build a solid case for adopting this technology, you need to track specific, measurable metrics. These data points provide concrete proof of how autonomous AI agents are performing and where they’re delivering the most significant value.
Here are a few key areas to keep an eye on:
- Reduced Operational Costs: Look at the drop in expenses tied to manual labour, fixing errors, and allocating staff to repetitive tasks. A finance agent, for example, could slash overtime hours needed for month-end closing.
- Accelerated Project Timelines: Measure the time saved on key business processes, whether it’s qualifying sales leads or screening job candidates in HR. Finishing these workflows faster means you get to the value quicker.
- Improved Data Processing Accuracy: Monitor the reduction in human error for data-heavy jobs like processing invoices or generating reports. Better accuracy means less costly rework and more reliable data for decision-making.
These metrics draw a straight line from your investment to the outcome, proving how agentic AI delivers real, measurable improvements.
By systematically tracking these KPIs, you can move past anecdotal success stories and create a data-driven narrative that justifies further investment. The numbers themselves tell a compelling story of improved productivity and business agility.
The Australian Context: Benefits and Hurdles
Across Australia, the adoption of autonomous AI agents is picking up speed, and the positive impacts are becoming clear. Many businesses are reporting major efficiency gains—some as high as 50%—in areas like customer service, sales, and HR. The main use case, making up around 64% of deployments, is focused on automating business processes to boost productivity. For a deeper dive, check out our guide on what is business process automation.
However, it’s not always a smooth journey. Around 62% of Australian companies looking into agents admit they don’t have a clear strategy from the outset, and a significant 32% of projects never make it past the pilot stage.
Strategic Impact Goes Beyond Just Saving Money
While efficiency gains are often the initial drawcard, the strategic impact of autonomous AI agents is just as important. By automating entire workflows, businesses can become far more agile and responsive to shifts in the market.
Think about a supply chain agent. It doesn’t just flag a disruption; it can autonomously vet and coordinate with alternate suppliers to keep things moving. This capability doesn’t just save money on one delayed shipment—it builds a more resilient, adaptive supply chain that gives you a serious competitive edge.
Ultimately, the goal is to build a smarter, more proactive organisation. Autonomous AI agents are a key part of that puzzle, handling the complex operational details so your human teams can focus on steering the ship and planning for what’s next.
A Framework for Weaving AI Agents into Your Business
Bringing autonomous AI agents into a business isn’t like installing a new piece of software. You can’t just ‘plug and play’. It’s a deliberate, structured process that needs to balance big ambitions with a healthy dose of pragmatism. A solid framework is your best friend here—it helps manage the complexity, sidestep the risks, and make sure the technology actually delivers what it promises. Jumping in without a clear plan is a surefire way to end up with a stalled project and a hole in your budget.
Think of it less as a tech task and more as a strategic business initiative. This means getting serious about planning pilot projects, shoring up your data infrastructure, and figuring out the crucial dynamic between your team and their new digital colleagues. A phased rollout lets you learn, adapt, and build confidence with each step, setting the stage for a successful, organisation-wide implementation.
Start with a Strategic Pilot Project
The first move in any smart integration is a well-defined pilot project. The aim isn’t to overhaul the entire company overnight. It’s about scoring a quick, measurable win in a controlled space. This success builds momentum and teaches you invaluable lessons for the more ambitious rollouts to come.
Your best bet is to pick a process that’s high-impact but relatively low-risk. Often, the perfect candidates are those notoriously manual, repetitive workflows that everyone knows are a major operational bottleneck.
To zero in on the right pilot, ask yourself these questions:
- Can we measure success? You need to be able to quantify the impact. Think in concrete terms: hours saved, errors slashed, or tasks ticked off.
- Is the scope contained? The project needs clear boundaries. It shouldn’t rely on a dozen other complicated systems to work.
- Is there a strong business case? The benefit should be obvious and get key stakeholders nodding in agreement.
This first project is your proof-of-concept. It demonstrates the real-world value of autonomous AI agents and helps you get the wider buy-in needed to take the initiative further.
Get Your Data and Security in Order
An autonomous agent is only ever as sharp as the data it can get its hands on. Before you even think about deploying an agent, you have to be sure your data infrastructure is ready for it. This means your data must be clean, accessible, and correctly permissioned. An agent trying to make sense of inaccurate or siloed information is doomed from the start.
Security, of course, can’t be an afterthought. You need robust protocols in place to govern how agents access and use sensitive information. This means defining clear access controls, implementing thorough logging to track every agent action, and making sure all data handling complies with privacy laws.
An autonomous agent operates with a degree of independence, making it imperative that its operational “playground” is secure. Establishing clear security guardrails from the outset is non-negotiable for responsible integration.
Establish Clear Governance and Oversight
Once agents start tackling more complex jobs, a clear governance model becomes absolutely critical. This framework needs to spell out who is responsible for watching agent performance, who gets to decide when to expand their duties, and what happens when an agent hits a problem it can’t solve.
A key part of this is building a human-in-the-loop system for the really important decisions. While autonomy is the goal, strategic human oversight ensures agents operate ethically and stay aligned with your business objectives. This step is often overlooked, but it’s fundamental to scaling these systems safely and effectively. Professional guidance can be a game-changer here; exploring expert AI consulting services can help you build a robust governance framework that fits your organisation like a glove.
The rapid uptake of this technology really highlights the need to get this right. It’s expected that by mid-2025, nearly 80% of Australian organisations working with AI will have deployed autonomous agents. This isn’t just a tech trend; it’s being driven by high expectations, with 62% of these companies forecasting returns greater than 100% on their agentic AI investments. This strategic shift underscores just how important it is to prioritise governance from day one to ensure these powerful systems are scaled responsibly. You can discover more insights about agentic AI statistics to see how quickly this is moving in the Australian enterprise space.
Manage the Human-Agent Collaboration
Finally, a successful integration hinges on people. Introducing autonomous agents will undoubtedly change how your teams operate. It’s absolutely vital to frame this shift not as a replacement for people, but as an augmentation of their capabilities.
Invest in proper training to help your employees understand how to work alongside these new digital colleagues. Teach them how to delegate tasks effectively, make sense of an agent’s output, and step in when needed. By fostering a culture of collaboration, you empower your team to use agents as powerful tools—tools that free them from tedious work and let them focus on the more strategic, high-value activities that truly move the needle. This approach makes for a much smoother transition and ensures you get the maximum productivity boost from your investment.
Preparing for the Future of Autonomous Business
The path forward with autonomous AI agents isn’t a straight line to a finish line; it’s more like a commitment to constant evolution. As these agents become more sophisticated, their impact is going to grow in ways we’re only just beginning to imagine. We’re heading towards a future where systems of multiple agents work together on incredibly complex problems, operating like a high-performing human team to solve challenges far beyond what any single agent could handle today.
This reality shifts the entire strategic conversation for business leaders. It’s no longer about just adopting a new piece of tech. Instead, it’s about nurturing a culture of continuous adaptation. Bringing autonomous AI agents into the fold isn’t a simple IT upgrade; it’s a fundamental reimagining of how your business operates, from the ground up. True success will come from an organisation’s ability to learn and grow alongside its AI, constantly refining how things are done based on the new insights and efficiencies that are unlocked.
Your Strategic Imperative
The critical question has moved beyond if you should get involved with this technology, to how and when. If you want to build a real, lasting competitive advantage in an increasingly automated world, you need to start planning now. Businesses that wait on the sidelines risk being completely outmanoeuvred by more agile competitors who are already weaving intelligent automation into the fabric of their operations.
The question for leaders isn’t whether autonomous agents will reshape their industry, but how they will guide that change. Waiting isn’t a strategy; it’s a decision to be left behind.
The best way to start is small. Pinpoint a high-impact, low-risk area of the business where an autonomous agent could deliver some quick, obvious value. This gives you a practical training ground, builds crucial internal momentum, and provides the proof-of-concept you need for wider adoption. The time to start that strategic planning is now, to secure your place in the future of business.
Your Questions About AI Agents, Answered
Diving into the world of autonomous AI agents naturally brings up some practical questions. How do they really work? Are they secure? What does it take to get them running? These are exactly the kinds of questions business leaders should be asking. Let’s clear up some of the most common ones.
How Are Autonomous AI Agents Different From RPA?
This is a classic point of confusion, and it’s an important one to get right. While both are forms of automation, they operate on completely different levels of intelligence.
Think of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) as a digital assembly line worker. It’s fantastic at mimicking repetitive, rule-based human actions with precision—like copying data from a spreadsheet into your CRM. It follows a strict script, and that’s it.
An autonomous AI agent, however, is more like a digital project manager. You give it a high-level goal, and it figures out the steps to get there. It can reason, plan, and adapt its approach when it hits a roadblock, something an RPA bot simply can’t do.
The real distinction is autonomy. RPA follows a fixed set of instructions, no matter what. An autonomous agent uses its reasoning ability to decide on the best course of action to achieve a goal.
What Happens When an AI Agent Makes a Mistake?
It’s a fair question—what if it gets something wrong? This is a core concern, and effective autonomous agent systems are built with safety nets and human oversight in mind. When an agent runs into a problem it can’t solve or an action fails, it’s designed to either try another path or, crucially, flag the issue for a human team member to review.
Everything is designed for traceability. Every decision and action the agent takes is logged, creating a clear audit trail. This makes it easy to find out exactly what went wrong, correct the agent’s logic, and make sure the same error doesn’t happen twice.
Are Autonomous AI Agents Secure?
Security isn’t an add-on; it’s baked into the design from the very beginning. Autonomous agents don’t get free rein over your systems. They operate within strict boundaries set by your IT team, with access to data and systems governed by the same robust security protocols you’d apply to a human employee.
Here are some of the core security measures:
- Access Controls: Agents are only given permission to access the specific data and tools they absolutely need for their job. Nothing more.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Your existing policies are enforced to stop sensitive information from being shared or handled incorrectly.
- Robust Authentication: Secure protocols make sure that only authorised agents can interact with your business systems.
These guardrails ensure that while the agent works independently, it’s always within a secure, controlled environment that respects your organisation’s data governance policies.
Can AI Agents Work With Our Existing Systems?
Yes, absolutely. This is one of their biggest strengths. A key capability of autonomous AI agents is their knack for integrating with and orchestrating tasks across all sorts of different software. They use APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) and other connectors to “talk” to your existing CRM, ERP, finance software, and just about any other system you rely on.
This ability to work with the tools you already use is what makes them so valuable. They become a unifying force, automating complex processes that jump between different departments and applications, all without you needing to rip out and replace your current tech stack.
Ready to explore how autonomous AI agents can reshape your business efficiency? Osher Digital specialises in developing custom AI and workflow automations that drive efficiency and scale. Learn more about our AI solutions.
Jump to a section
Ready to streamline your operations?
Get in touch for a free consultation to see how we can streamline your operations and increase your productivity.